Customers are asked a simple question about their likelihood of recommending your product or service to friends and colleagues, and this information is used to calculate NPS. Reactions are divided into three groups: supporters, supporters, and detractors.
The percentage of critics in the survey findings is subtracted from the number of promoters to determine your net promoter score (NPS). NPS is a potent business indicator facilitating growth and identifying factors influencing customer loyalty.
Promoter Score
NPS is a well-liked customer experience (CX) indicator that forecasts growth and gauges loyalty. It is determined by asking consumers in a survey how likely they are to suggest your brand to others following an engagement with your product or service. Next, survey participants are divided into promoters, detractors, and passives. The percentage of critics is subtracted from the percentage of promoters to arrive at the final NPS.
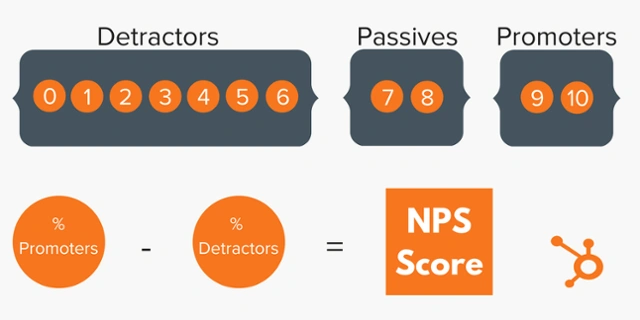
NPS questionnaires can be made to include one or more questions. On a scale of 0 to 10, respondents are asked to rate their likelihood of suggesting your product or service to others in an introductory NPS survey. Respondents who score you 9 or 10 are Promoters. Those who give you a six or below are Detractors. Those who give you a 7 or 8 are Passives.
The goal is to have more Promoters than Detractors and Passives. Promoters are your brand ambassadors who can fuel growth by recommending you to their friends and family. The best way to increase your NPS is by creating a customer experience that exceeds customers’ expectations and encourages them to share their positive experiences with others.
Detractor Score
As you gather customer responses, segregate the promoters (scores of 9 or 10) and detractors (scores of 0-6). The net promoter score calculation can be done manually, in Excel or Google Sheets.
According to Bain, a high NPS score indicates that many customers are advocates for your business and will refer others to you or increase their purchase volume and frequency. The detractors, conversely, are likely to steer friends and colleagues away from your product or service or, even worse, switch to competitors.
The Passives are a group of people who are neither Promoters nor Detractors, but they’re also not enthusiastic about your business either. The good news is that this group represents an excellent opportunity to build customer loyalty, as you can turn them into Promoters by improving their buying experience.
A low NPS score is a red flag, indicating some customer problems to address. It’s essential to track the NPS score over time and understand what’s driving it up or down so you can make confident decisions. You can also use NPS as a competitive benchmark to identify new growth opportunities. This is possible because NPS results are comparable across industries.
Passive Score
In NPS surveys, customers are asked to rate how likely they are to recommend a product or service to others. The responses are then categorized as Detractors (0-6), Passives (7-8), and Promoters (9-10). A company’s Net Promoter Score is calculated by subtracting the Detractors’ percentage from the Promoters’.
A business’s NPS is essential for several reasons, including that it is a good predictor of future customer growth. NPS also helps companies identify opportunities to delight customers.
When NPS scores are high, customers are likelier to become brand advocates and fuel growth. But when NPS scores are low, it’s a clear sign that more work needs to be done to create happy customers.
NPS can also help businesses spot problems before they become a crisis, much like sonar on a ship. By analyzing NPS results and comparing them to competitors, companies can see trends and spot areas of opportunity. Businesses can enhance customer happiness and increase net promoter score (NPS) by determining the underlying reasons behind negative reviews. In addition, NPS allows for a more in-depth qualitative analysis of what customers are thinking. This can lead to more precise follow-ups and effective strategies for addressing customer concerns. This, in turn, can have a positive impact on revenue. NPS can be a crucial indicator of a business’s financial health.
Key Drivers
When gauging client loyalty, one of the most important indicators is the Net Promoter Score (NPS). It is a metric that measures how likely customers are to recommend you to others and can help you predict business growth.
The question “How likely are you to recommend our company/product/service to a friend or colleague?” is used to compute NPS from survey answers. Respondents are then categorized into three groups: Detractors (0-6 or 1-3 on a scale of 5 points), Passives (7-8 or 4 on a scale of 5 points), and Promoters (9-10 or 5 on a scale of 5-point). You calculate your NPS by subtracting the percentage of Detractors from the percentage of Promoters.
This simple formula will give you an accurate picture of your customer loyalty. It will also allow you to identify areas that need improvement, which is critical in maintaining a high NPS.
For example, let’s say your best friend tells you she recently surveyed her realtor and gave them a low rating because they didn’t take her calls, didn’t follow up quickly enough, and made significant mistakes. She is likely only to use or refer this realtor to some. This is a Detractor, and she can negatively affect your business.
Learning the critical drivers of NPS allows you to identify which customers are most loyal to your brand and how to create an environment that will keep them coming back. This is the most cost-effective way to market your business and build your brand!